Specifications:
Product information: Deep Upper Limb and hand
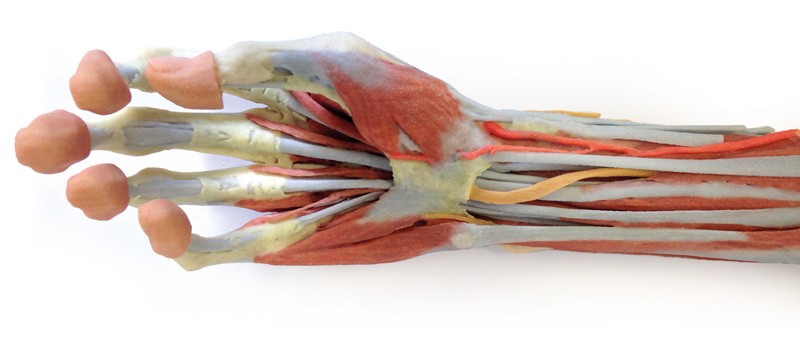
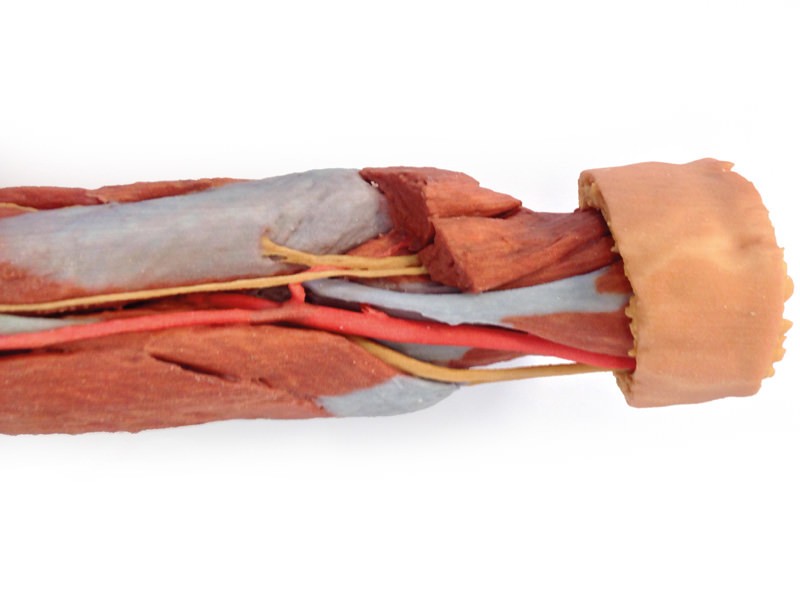
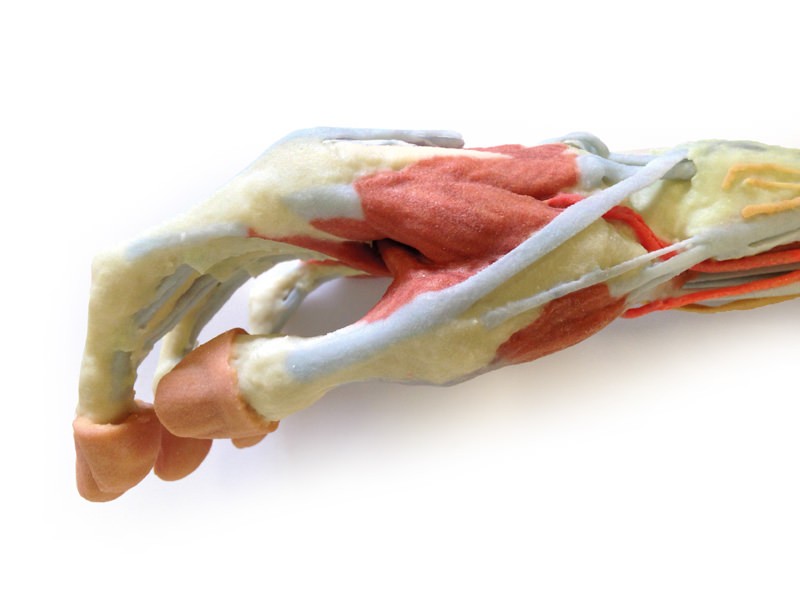
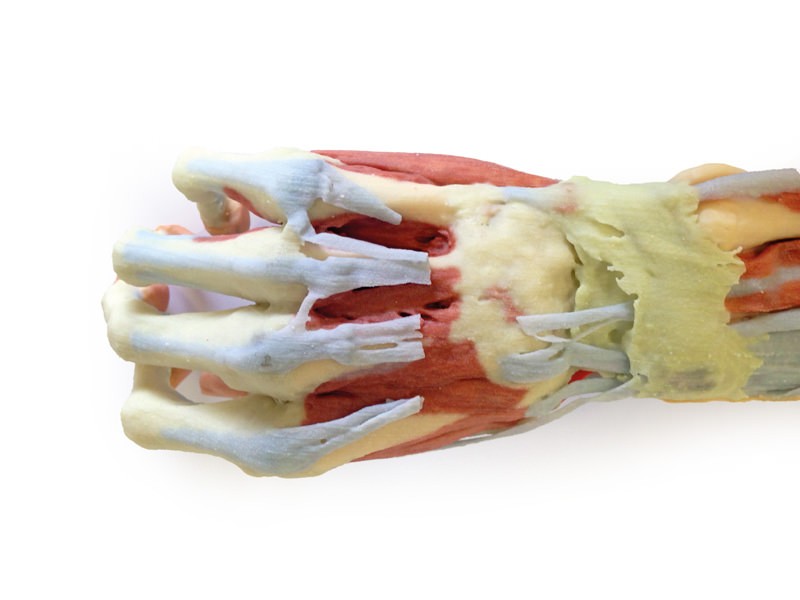
This 3D print of a superficially dissected right upper limb specimen displays a mixture of the vascular, nervous and muscular anatomy of the distal arm, forearm and hand. In the distal arm and elbow/cubital fossa region we can see the arrangement of the biceps tendon, brachial artery and median nerve from lateral to medial. The bicipital aponeurosis has been removed to reveal the structures deep to it within the cubital fossa. The ulnar nerve has been reflected from the cubital tunnel to demonstrate its pathway adjacent to the medial epicondyle. The brachioradialis and extensor carpi radialis longus have been sectioned close to their origins to expose the radial nerve, the superficial branch of the radial nerve, and the deep branch of the radial nerve piercing the supinator muscle. In the forearm, the superficial flexor muscles arising from the common flexor origin can be clearly seen (from lateral to medial– pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis (FCR), flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) and flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU)). There is not a palmaris longus muscle in this cadaver. The radial artery is clearly identifiable with the brachioradialis muscle largely removed. The ulnar artery is not visible in this preparation. On the posterior aspect of the forearm the extensor muscles arising from the common extensor origin are clearly identifiable. These include (from medial to lateral) the extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU), extensor digiti minimi, extensor digitorum and extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) lying beneath the cut tendon of ECRL. The extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) can be seen arising from the inferior aspect of the lateral supracondylar ridge but only about 2-4 cm of its muscle origin remain. Further distally the abductor pollicis longus (APL) and extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) can be seen emerging from deep to superficial and ‘wrapping’ around the radius. They, along with extensor pollicis longus (EPL), travel distally to insert into the extensor or dorsal surface of the base of the 1st metacarpal, proximal phalanx and distal phalanx of the thumb, respectively. The EPL tendon disappears under the extensor retinaculum and part of it has been dissected at the snuff box to expose the radial artery in the floor of the anatomical snuffbox. Stumps of the cutaneous branch of the radial nerve lie just proximal to its roof which has been dissected and removed. The extensor retinaculum is clearly visible on the dorsum of the wrist and distal to it the tendons of extensor indicis and ECRB and ECRL can be seen inserting into the 2nd and 3rd metacarpals. The ED tendons are transected in the midcarpal region On flexor surface of the hand, a deep dissection reveals muscles of the thenar and hypothenar eminences, the flexor retinaculum of the hand (roof of the carpal tunnel with the median nerve disappearing deep to it), the long tendons of the hand, the lumbricals and the interossei muscles. A superficial palmar branch of the radial artery passes over the flexor retinaculum partly piercing the abductor pollicis brevis muscle close to its origin.
Catalogue: PDF
See more products OpenMedis brand.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.