Specifications:
Further Information
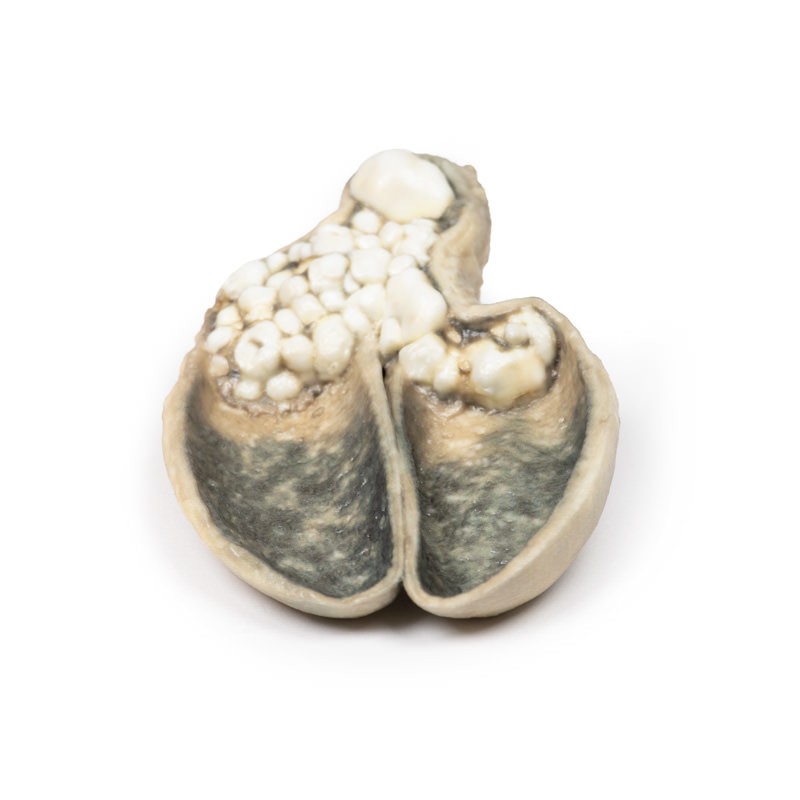
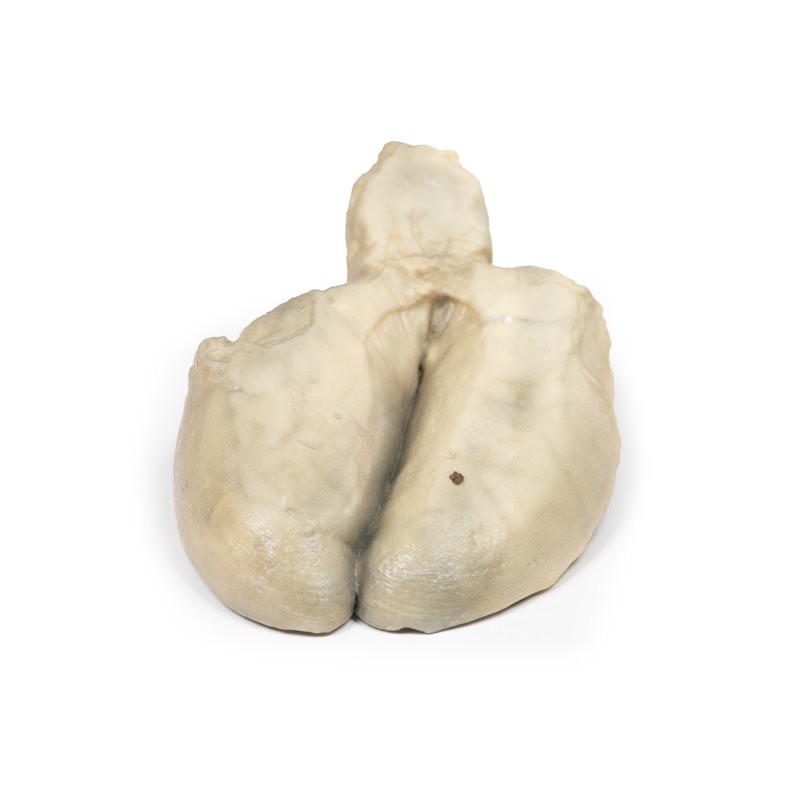
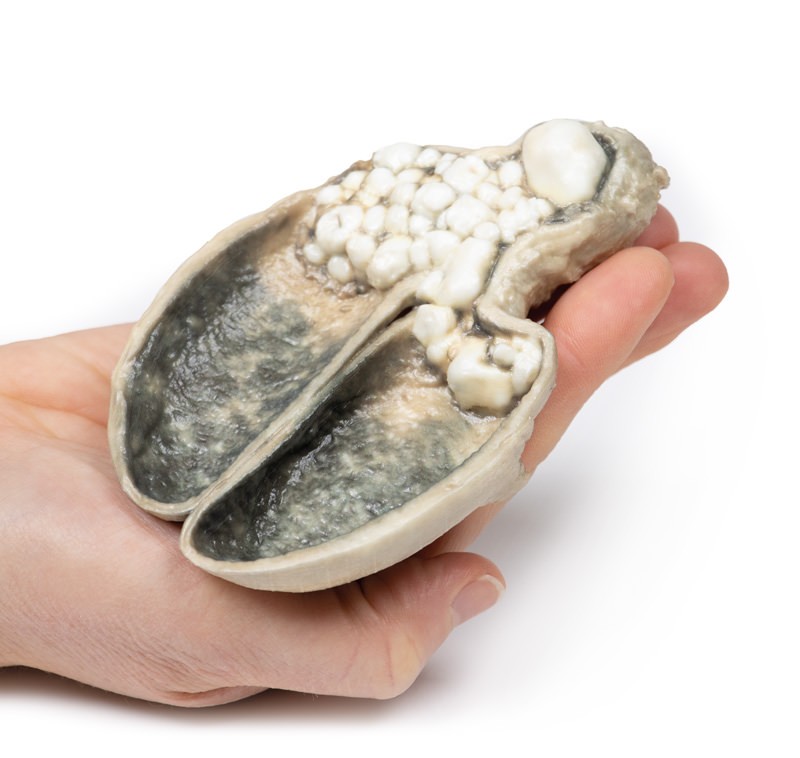
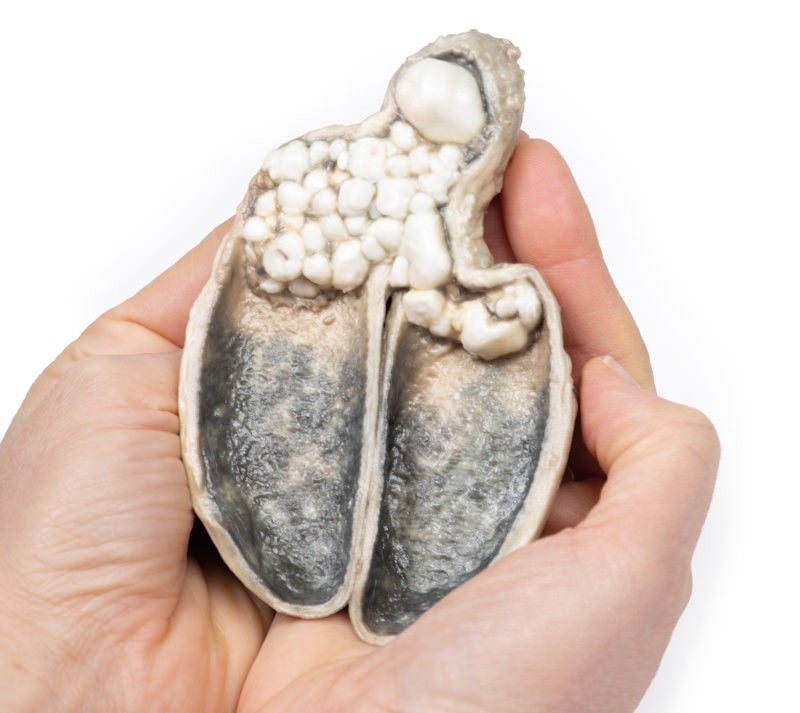
Gallstones account for the vast majority of acute cholecystitis, with only 5 – 10% of cases being due to other pathology. Chronic cholecystitis may occur, resulting from recurrent attacks and causing fibrosis and thickening of the gallbladder wall. 6-11% of patients with symptomatic gallstones will go on to develop acute cholecystitis. Serum biochemistry will demonstrate leucocytosis with or without obstructive liver function tests. Ultrasound will demonstrate gallstones in the gallbladder, along with wall thickening and a sonographic Murphy’s sign (tenderness from the pressure of the ultrasound probe). Other imaging modalities include nuclear medicine cholescintography scans, MRCP (magnetic cholangiopancreatography) and CT. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) will provide diagnostic information regarding biliary obstruction and may also be therapeutic. Causative organisms (if present) will be from the gut flora, commonly E coli, Enterococcus, Klebsiella and Enterobacter. Complications include gangrenous cholecystitis, perforation, cholecystoenteric fistula or gallstone ileus. Definitive treatment is surgical cholecystectomy.
Catalogue: PDF
See more products OpenMedis brand.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.